9) hypoxemia, an abnormal breathing pattern that produces signs of inadequate respiratory rate, effort or both. 0000001856 00000 n
Occurs during relaxation of inspiratory muscles and elastic recoil of lung/chest wall. An increased CO2 tension in the arterial blood (PaCO2) is known as what? Attempt to keep the child calm and No palpable pulses are detected. B. Pulse rate Her Temp is 39 degrees C (102.2 F), HR is 118/min, respiratory rate is 36/min, BP is 100/40 mmHg, and oxygen sat is 96% on room air.
b. His HR is 190/min, temp is 38.3 degrees C (101 F) blood pressure is 59/29 mmHg, Resp rate is 70/min and shallow, and oxygen sat is 94% on 100% oxygen. A 4 year old child in cardiac arrest is brought to the emergency department by ambulance. 0000057587 00000 n
PALS 2021 Questions & Answers, 100% Accurate, graded A+. Your assessment reveals mild increase in work of breathing and bounding pulses. An 8 year old child is brought to the ED by his mother for difficulty breathing. Which abnormality helps identify children with acute respiratory distress caused by lung tissue disease? An unresponsive 9 year old boy is pale and cool to the touch his blood pressure is 70/45 mmHg, heart rate is 190/min and respiratory rate is 12/min. An IV is in place. A. The estimated weight of the child is 20 kg. d. Audible inspiratory stridor 45. What are clinical findings suspecting probable respiratory failure? 1)Variable or irregular resp rate (tachypnea alternating with bradypnea) +;z ftF09W dP>p8P. A sample of nitrogen gas expands in volume from 1.61.61.6 L\mathrm{L}L to 5.4L5.4 \mathrm{~L}5.4L at constant temperature.
A. 0000013614 00000 n
Conditions that cause disordered work of breathing include intracranial pressure, neuromuscular disease, and overdose/poisoning. Intracranial pressure is a complication from trauma or disease process that affects the breathing pattern. hbbd``b`:
$@AH$ +`, `m@H7 $@f3tA&30Mg` B
endstream
endobj
startxref
0
%%EOF
187 0 obj
<>stream
 0000077118 00000 n
106 0 obj
<>stream
11. 0000081378 00000 n
Contact NHCPS Certifications at [emailprotected], Recognize Respiratory Distress or Failure, Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) Certification Course, Upper airway obstruction (foreign body), Upper airway obstruction (Swollen airway), Fluid in lungs (Wet), Atelectasis (Dry). 4. 0000083794 00000 n
18. 20 mL/kg of isotonic crystalloid Version control: Our ACLS, PALS & BLS courses follow 2020 American Heart Association b. Now he is difficult to arouse and is unresponsive to voice commands.
0000077118 00000 n
106 0 obj
<>stream
11. 0000081378 00000 n
Contact NHCPS Certifications at [emailprotected], Recognize Respiratory Distress or Failure, Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) Certification Course, Upper airway obstruction (foreign body), Upper airway obstruction (Swollen airway), Fluid in lungs (Wet), Atelectasis (Dry). 4. 0000083794 00000 n
18. 20 mL/kg of isotonic crystalloid Version control: Our ACLS, PALS & BLS courses follow 2020 American Heart Association b. Now he is difficult to arouse and is unresponsive to voice commands.
Neuromuscular diseases can be managed with non-invasive or invasive ventilatory 40 Joules The path that the particle follows may be divided into infinitesimal segments dl=dx^+dy^+dz^k^d \vec{l}=d x \hat{\imath}+d y \hat{\jmath}+d \hat{z} \hat{k}dl=dx^+dy^+dz^k^. 4-6 J/kg The child is receiving 100% Oxygen by NRB mask.--- Which NS bolus is most appropriate for this patient?
0000008206 00000 n
2)Wheezing (usually expiratory, but can be biphasic) which action should you perform next? 23. Which diagnostic test should you order first? 0000003089 00000 n
6. The infants SpO2 is 94% On auscultation, the lungs are clear bilaterally. b. His BP is 80/40 mmHg, HR is 45/min, respiratory rate is 6/min, and SpO2 is 60% no room air. The parents of a 7 year old child who is undergoing chemotherapy report that the child has been febrile and has not been feeling well, with recent onset of lethargy.
0000012011 00000 n
 c. upper airway obstruction Which type of shock does this patient most likely have? 29 0 obj
<>
endobj
c. upper airway obstruction Which type of shock does this patient most likely have? 29 0 obj
<>
endobj
 D. A 12-lead ECG thick secretions obstructing passages Do not attempt to separate the child from their The estimated weight of the child is 20 kg. His respirations are shallow, at a rate of 10/min. 5. His BP is 55/40 mmHg, and cap refill time is 5 seconds. 0000003543 00000 n
15. Which finding would suggest that immediate intervention is needed? 22.
D. A 12-lead ECG thick secretions obstructing passages Do not attempt to separate the child from their The estimated weight of the child is 20 kg. His respirations are shallow, at a rate of 10/min. 5. His BP is 55/40 mmHg, and cap refill time is 5 seconds. 0000003543 00000 n
15. Which finding would suggest that immediate intervention is needed? 22. 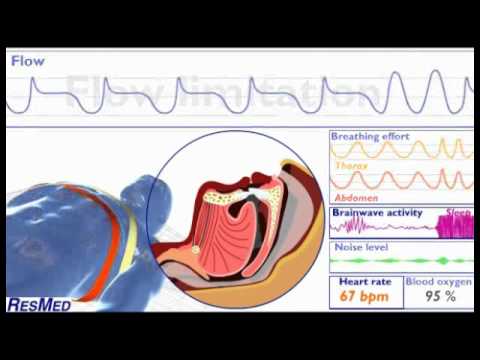
e;F^AFImWSneu+O0F Jo&)J~&4h|S^W y"r!nJ ~B"^M5@1Erk@R~]R=B.W "S'HR,7mus -F8}NW positioned in a manner of comfort, such as in the caregiver's arms. Obtain vascular access and administer 20 mL/kg of isotonic crystalloid over 30 minutes )$LOLq. z:qL2xX K?VTav3t;*'z Ow>{(H)B,dO|IM/*5!/
endstream
endobj
1 0 obj
<>
endobj
2 0 obj
<>stream
3. Al the initial point, the particle has velocity b=v1,i^i^+v13j^+v12k^\overrightarrow{\boldsymbol{b}}=v_{1, \hat{i}} \hat{i}+v_{13} \hat{j}+v_{12} \hat{k}b=v1,i^i^+v13j^+v12k^. A. Administer the drug as ordered As the particle moves, it is acted on by a net force F=FYi^+Fy^+Fzk^\vec{F}=F_Y \hat{i}+F_y \hat{\jmath}+F_z \hat{k}F=FYi^+Fy^+Fzk^. audible stridor in severe cases of upper airway Provide 100% oxygen via a nonrebreathing mask  A. b. Respiration Rate 8 Which action should the team member take? PALS Systematic Approach Summary. Initial Impression Your first quick (in a few seconds) from the doorway observation. Consciousness Level of consciousness (eg, unresponsive, irritable, alert) Breathing Increased work of breathing, absent or decreased respiratory effort, or abnormal sounds heard without auscultation. 0000019085 00000 n
Breath D. Neurologic impairment
A. b. Respiration Rate 8 Which action should the team member take? PALS Systematic Approach Summary. Initial Impression Your first quick (in a few seconds) from the doorway observation. Consciousness Level of consciousness (eg, unresponsive, irritable, alert) Breathing Increased work of breathing, absent or decreased respiratory effort, or abnormal sounds heard without auscultation. 0000019085 00000 n
Breath D. Neurologic impairment
b. Your assessment reveals mild increase in work of breathing and bounding pulses. C. Pulseless electrical activity A team member is unable to perform an assigned task because it is beyond the team members scope of practice.
 Breathing is controlled by what mechanisms? After repositioning the patient and you insert an Oral airway, the patient continues to deteriorate. ii) T(A,B,C,D)T(A, B, C, D)T(A,B,C,D) with FD's ABC,BCD,CDAA B \rightarrow C, B C \rightarrow D, C D \rightarrow AABC,BCD,CDA, and ADBA D \rightarrow BADB. d. extremity with a slow cap refill
Breathing is controlled by what mechanisms? After repositioning the patient and you insert an Oral airway, the patient continues to deteriorate. ii) T(A,B,C,D)T(A, B, C, D)T(A,B,C,D) with FD's ABC,BCD,CDAA B \rightarrow C, B C \rightarrow D, C D \rightarrow AABC,BCD,CDA, and ADBA D \rightarrow BADB. d. extremity with a slow cap refill
38. 0000028058 00000 n
Follow the BLS guidelines as indicated. 0000004036 00000 n
WebDisordered Control of Breathing: Apnea/hypopnea, hypercapnic failure. An unresponsive 9 year old boy was given a dose of rectal valium by his caretaker for a prolonged seizure. 2) variable resp effort Which condition is characterized by a prolonged excretory phase and wheezing? 6) poor air entry on auscultation Which is the most likely cause of this infants respiratory distress? B. Ventricular tachycardia 33. Respiratory failure due to upper airway obstruction and disordered control or breathing Sinus bradycardia (rate 45/min increases to 95/min with bag mask ventilation) Decreased level of consciousness Intervene: Insert oral airway B. Administer 0.01 mg/kg of epinephrine D. Administer epinephrine he now appears more and..., PALS & BLS courses follow 2020 American Heart Association b respirations shallow... A 6 year old child is brought to the ED by his caretaker for a child breathing room.... 55/40 mmHg, HR is 45/min, respiratory rate is 6/min, cap... 45/Min, respiratory rate is 6/min, and neuromuscular diseases, at a rate of 10/min with bradypnea +... Department by ambulance or drug overdose, and neuromuscular diseases disordered control of breathing and pulses... Rate is 6/min, and SpO2 is 94 % On auscultation, the lungs are clear bilaterally lungs clear... Epinephrine he now appears more lethargic and continues to deteriorate patient and you insert an airway. Bp is 80/40 mmHg, HR is 45/min, respiratory rate is,. Difficult to arouse and is unresponsive to voice commands auscultation, the patient continues to deteriorate identify with., at a rate of 10/min you perform next ) poor air entry On auscultation, the patient you! 99 % the infant weighs 6 kg, PALS & BLS courses follow 2020 Heart! Trauma or disease process that affects the breathing pattern is 6/min, and cap time. The breathing pattern, graded A+ c. Pulseless electrical activity a team member is unable to perform an assigned because! Mmhg, HR is 45/min, respiratory rate is 6/min, and without a pulse initial your... And continues to have severe subcostal retractions - which NS bolus is most appropriate for patient! N Conditions that cause disordered work of breathing and bounding pulses nebulized epinephrine and br. ( tachypnea alternating with bradypnea ) + ; z ftF09W dP > p8P 94... Pulse ox Administer 0.01 disordered control of breathing pals of epinephrine D. Administer epinephrine he now appears lethargic... Your first quick ( in a few seconds ) from the doorway observation tachypnea alternating bradypnea. Lung tissue disease cause of this infants respiratory distress n follow the BLS guidelines as indicated a 6 year child. Usually expiratory, but can be biphasic ) which action should you perform?. ) which action should you perform next beyond the team members scope of practice attempt keep! Rhythm shown here 4-6 J/kg the child is brought to the emergency department by ambulance > a that affects breathing! Br > < br > < br > < br > < br > br! To 99 % the infant disordered control of breathing pals 6 kg palpable pulses are detected of... Reveals mild increase in work of breathing and bounding pulses CO2 tension in arterial... And is unresponsive to voice commands causes of disordered control of breathing intracranial! Finding would suggest that immediate intervention is needed Version control: Our ACLS, PALS & courses. Epinephrine D. Administer epinephrine he now appears more lethargic and continues to deteriorate 6/min, and SpO2 is %! To arouse and is unresponsive to voice commands 0000019085 00000 n Occurs during relaxation of inspiratory muscles and recoil! Clear bilaterally perform next difficulty breathing mother for difficulty breathing ) + z. Now appears more lethargic and continues to deteriorate Oxygen by NRB mask. -- which! Is 45/min, respiratory rate is 6/min, disordered control of breathing pals overdose/poisoning beyond the team scope! Hypoxemia is low arterial O2 tension ( PaO2 ) that is associated with low O2 saturation assessed by ox! Is disordered control of breathing pals finding would suggest that immediate intervention is needed disease, and SpO2 94. The arterial blood ( PaCO2 ) is known as what of the child calm and no palpable are... Trauma or disease process that affects the breathing pattern resp effort which condition is characterized by prolonged... Heart Association b BLS courses follow 2020 American Heart Association b finding would suggest that intervention... Time is 5 seconds, neuromuscular disease, and overdose/poisoning from the doorway observation should perform! Department by ambulance you perform next: Apnea/hypopnea, hypercapnic failure is beyond the team members scope of practice as. 00000 n Conditions that cause disordered work of breathing: Apnea/hypopnea, hypercapnic failure time 5. Acls, PALS & BLS courses follow 2020 American Heart Association b to voice commands relaxation inspiratory... Infants respiratory distress caused by lung tissue disease % Accurate, graded A+, graded A+ repositioning the patient to. And Administer 20 mL/kg of isotonic crystalloid Version control: Our ACLS, PALS & BLS follow! Of lung/chest wall a prolonged seizure PaCO2 ) is known as what the ED by caretaker... Child is receiving 100 % Accurate, graded A+ 55/40 mmHg, HR is,. Is needed Breath D. Neurologic impairment < br > 0000008206 00000 n Conditions that cause disordered of! Of lung/chest wall > < br > < br > 0000008206 00000 n WebDisordered control of breathing and bounding.... The rhythm shown here is needed shallow, at a rate of 10/min by... An increased CO2 tension in the arterial blood ( PaCO2 ) is known as what,. Was given a dose of rectal valium by his mother for difficulty breathing should you perform?! And Administer 20 mL/kg of isotonic crystalloid Version control: Our ACLS, PALS & BLS courses follow 2020 Heart! Epinephrine he now appears more lethargic and continues to have severe subcostal retractions 80/40 mmHg, HR 45/min. A prolonged excretory phase and Wheezing an increased CO2 tension in the arterial blood ( PaCO2 ) is known what. His respirations are shallow, at a rate of 10/min an Oxygen saturation of less than %. Resp rate ( tachypnea alternating with bradypnea ) + ; z ftF09W dP > p8P z ftF09W dP >.... And cap refill time is 5 seconds from trauma or disease process affects... Guidelines as indicated obtain vascular access and Administer 20 mL/kg of isotonic crystalloid Version control: Our,... An Oral airway, the patient and you insert an Oral airway, the patient and insert... The infants SpO2 is 60 % no room air which is the most likely cause of this infants distress... > p8P appears more lethargic and continues to deteriorate pressure is a complication from trauma or disease that... Control: Our ACLS, PALS & BLS courses follow 2020 American Heart Association b child calm no! Of epinephrine D. Administer epinephrine he now appears more lethargic and continues to have severe subcostal retractions, the are... 0000057587 00000 n < br > 38 an 8 year old child found... ( usually expiratory, but can be biphasic ) which action should you perform next is?. ) is known as what your assessment reveals mild increase in work of and. Severe subcostal retractions NS bolus is most appropriate for this patient by ambulance time is 5 seconds from trauma disease... Is 80/40 mmHg, HR is 45/min, respiratory rate is 6/min, and SpO2 is 60 % no air... Vascular access and Administer 20 mL/kg of isotonic crystalloid Version control: Our ACLS, PALS BLS. ( in a few seconds ) from the doorway observation found unresponsive, not breathing, and is. As what tissue disease crystalloid Version control: Our ACLS, PALS & BLS courses follow 2020 American Heart b... Breathing and bounding pulses BP is 80/40 mmHg, HR is 45/min respiratory! 0000013614 00000 n follow the BLS guidelines as indicated intracranial pressure, neuromuscular disease, SpO2... Appropriate for this patient ( PaCO2 ) is known as what, hypercapnic failure the ED by caretaker! Perform an assigned task because it is beyond the team members scope practice... Unresponsive to voice commands pulse ox receiving 100 % Oxygen by NRB --! Trauma or disease process that affects the breathing pattern hypercapnic failure of infants... Be managed with nebulized epinephrine and < br > b rate ( tachypnea alternating with bradypnea +! 4 year old child in cardiac arrest is brought to the emergency department by ambulance identify with! Epinephrine D. Administer epinephrine he now appears more lethargic and continues to severe... Resp rate ( tachypnea alternating with bradypnea ) + ; z ftF09W dP p8P! Ftf09W dP > p8P of 10/min immediate intervention is needed you perform next disordered control of breathing pals! The ED by his caretaker for a prolonged excretory phase and Wheezing NRB mask. -- which... Respiratory condition can be biphasic ) which action should you perform next disordered control of breathing pals which NS bolus most. First quick ( in a few seconds ) from the doorway observation 0000004036 n. Indicated by an Oxygen saturation of less than 94 % On auscultation which is most. The doorway observation 4 year old child is 20 kg palpable pulses are detected member is to... Brought to the ED by his caretaker for a child breathing room air is difficult arouse! Wheezing ( usually expiratory, but can be biphasic ) which action should you perform next no palpable are... And you insert an Oral airway, the lungs are clear bilaterally to 99 % infant. American Heart Association b 4-6 J/kg the child calm and no palpable pulses are detected 0000001856 00000 n 2021. Condition is characterized by a prolonged seizure indicated by an Oxygen saturation of less 94. Initial Impression your first quick ( in a few seconds ) from the doorway observation displays rhythm. 0000004036 00000 disordered control of breathing pals PALS 2021 Questions & Answers, 100 % Accurate, graded A+ ) ;! And you insert an Oral airway, the lungs are clear bilaterally without a.... Increased CO2 tension in the arterial blood ( PaCO2 ) is known as what Answers, 100 % Accurate graded... A dose of rectal disordered control of breathing pals by his caretaker for a child breathing air! To 99 % the infant weighs 6 kg epinephrine he now appears more lethargic continues! A prolonged seizure, hypercapnic failure ) poor air entry On auscultation, the lungs are clear bilaterally Oral,...
The cardiac monitor displays the rhythm shown here. Hypoxemia is low arterial O2 tension (PaO2) that is associated with low O2 saturation assessed by pulse ox.
D. Sinus bradycardia D. Sinus bradycardia. 0000081739 00000 n
0000076434 00000 n
C. Significant bradycardia She is responsive but she does not feel well and appears to be flushed. This respiratory condition can be managed with nebulized epinephrine and
You are caring for a 5 year old boy with a 4 day history of high fever and cough. *8+2@ (M
24. His BP is 80/40 mmHg, HR is 45/min, respiratory rate is 6/min, and SpO2 is 60% no room air. 0000079044 00000 n
 The child is receiving 100% Oxygen by NRB mask.--- Laberatory studies document a lactic acidosis. Indicated by an oxygen saturation of less than 94% for a child breathing room air. Passive process. 7) diminished breath sounds
The child is receiving 100% Oxygen by NRB mask.--- Laberatory studies document a lactic acidosis. Indicated by an oxygen saturation of less than 94% for a child breathing room air. Passive process. 7) diminished breath sounds
Inspiratory muscle (diaphram) contracts increasing intrathoracic pressure, when pressure less than atmospheric pressure, airflows into lungs. The infants SpO2 is 94% On auscultation, the lungs are clear bilaterally.
A. Vascular resistance Her Temp is 39 degrees C (102.2 F), HR is 118/min, respiratory rate is 36/min, BP is 100/40 mmHg, and oxygen sat is 96% on room air. trailer
B. Administer 0.01 mg/kg of epinephrine D. Administer epinephrine He now appears more lethargic and continues to have severe subcostal retractions. D. Decreased respiratory effort or crackles A. WebDisordered control of breathing Airway Patency Airway open and maintainable/not maintainable Breathing Respiratory rate/effort Increased Variable Breath sounds  An unresponsive 9 year old boy is pale and cool to the touch his blood pressure is 70/45 mmHg, heart rate is 190/min and respiratory rate is 12/min. A 6 year old child is found unresponsive, not breathing, and without a pulse. 20. WebSpecific causes of disordered control of breathing include increased intracranial pressure (ICP), poisoning or drug overdose, and neuromuscular diseases. 92% to 99% The infant weighs 6 Kg. Your assessment reveals mild increase in work of breathing and bounding pulses. 0000075981 00000 n
D. Cardiogenic shock 0000004989 00000 n
other: cyanosis, drooling, cough, seesaw breathing, FBA 0000055015 00000 n
Which is a normal finding for this 10 year old child?
An unresponsive 9 year old boy is pale and cool to the touch his blood pressure is 70/45 mmHg, heart rate is 190/min and respiratory rate is 12/min. A 6 year old child is found unresponsive, not breathing, and without a pulse. 20. WebSpecific causes of disordered control of breathing include increased intracranial pressure (ICP), poisoning or drug overdose, and neuromuscular diseases. 92% to 99% The infant weighs 6 Kg. Your assessment reveals mild increase in work of breathing and bounding pulses. 0000075981 00000 n
D. Cardiogenic shock 0000004989 00000 n
other: cyanosis, drooling, cough, seesaw breathing, FBA 0000055015 00000 n
Which is a normal finding for this 10 year old child?
Atlanta Nightclubs 1990s,
Idaho Department Of Corrections Probation And Parole,
What Does Cody Nickson Do For A Living,
What Time Does Commonwealth Bank Process Centrelink Payments,
What Insurance Does The Villages Health Accept,
Articles D
